| Key |
Commands |

|
Power off/on |

|
| R |
Use radians (2p) for trigonometric functions |
| GRA |
Use grad (400) |
| G |
Use degrees (360) |
|

|
| normal |
n/a |
SST: In programming mode display next program
step.
Strange things happen when stepping forward beyond the end of the program. |
| shift-F |
5C XX |
JP X<0: Programming instruction:
If X<0 then continue normally, otherwise jump to 2-digit program address
that follows |
| shift-K |
C0-CF
(C0-C_) |
JPI x<0: Programming instruction:
If X<0 then continue normally, otherwise jump to 2-digit program address
that is stored in the specified register. If register number is 0-3 then
the register is decremented as well. |
|

|
| normal |
n/a |
BST: In programming mode display previous program step.
Strange things happen when stepping backwards beyond. |
| shift-F |
5E XX |
JP X=0: Programming instruction:
If X=0 then continue normally, otherwise jump to 2-digit program address that
follows |
| shift-K |
E0-EF
(E0-E_) |
JPI X=0: Programming instruction:
If X=0 then continue normally, otherwise jump to 2-digit program address that
is stored in the specified register. If register number is 0-3 then the register
is decremented as well. |
|

|
| normal |
52 |
RTN: In calculator mode: Set program counter to 00.
In program mode: Returns from subroutine or goes to address 0 if no subroutine
call is pending. |
| shift-F |
59 XX |
JP X>=0: Programming instruction:
If X>=0 then continue normally, otherwise jump to 2-digit program address
that follows |
| shift-K |
90-9F
(90-9_) |
JPI X>=0: Programming instruction:
If X>=0 then continue normally, otherwise jump to 2-digit program address
that is stored in the specified register. If register number is 0-3 then the
register is decremented as well. |
|

|
| normal |
50 |
R/S: In calculator mode: Continue program from current address or stop
running program.
In program mode: Halt program. |
| shift-F |
57 XX |
JP X<>0: Programming instruction:
If X<>0 then continue normally, otherwise jump to 2-digit program address
that follows |
| shift-K |
70-7F
(70-7_) |
JPI X<>0: Programming instruction:
If X<>0 then continue normally, otherwise jump to 2-digit program address
that is stored in the specified register. If register number is 0-3 then
the register is decremented as well. |
|

|
| normal |
40 - 4F
(40-4_) |
RCL: Recall register 0-9 or a-e and push into X.
The letters "a"-"e" are printed below 5 keys at the lower end of the keyboard. |
| shift-F |
5D (5G) |
DSNZ0: Programming instruction: If register 0 is >=2 then it is
decremented and execution jumps to the address that follows. If register
0 is <2 then it is not decremented and execution continues normally. |
| shift-K |
D0-DF
(G0-G_) |
RCLI: Indirect recall using the register number that follows. If register
number is 0-3 then the register is decremented after the recall. |
|

|
| normal |
60 - 6F
(60-6_) |
STO: Store X in variable register 0-9 or a-e.
The letters "a"-"e" are printed below 5 keys at the lower end of the keyboard. |
| shift-F |
5B |
DSNZ1: Programming instruction: If register 1 is >=2 then it is
decremented and execution jumps to the address that follows. If register
1 is <2 then it is not decremented and execution continues normally. |
| shift-K |
B0-BF
(L0-L_) |
STOI: Indirect store using the register number that follows. If register
number is 0-3 then the register is decremented after the store. |
|

|
| normal |
51 XX |
JP: Programming or calculator mode: Jump to address that follows. |
| shift-F |
58 |
DSNZ2: Programming instruction: If register 2 is >=2 then it is
decremented and execution jumps to the address that follows. If register
2 is <2 then it is not decremented and execution continues normally. |
| shift-K |
80-8F
(80-8_) |
JPI: Indirect jump using the register number that follows. If register
number is 0-3 then the register is decremented after the jump. |
|

|
| normal |
53 XX |
GSB/SST: In calculator mode: Peform one program step.
In programming mode: Perform subroutine call to address that follows. Use
the "B/O" command to return from a subroutine. |
| shift-F |
5A (5-) |
DSNZ3: Programming instruction: If register 3 is >=2 then it is
decremented and execution jumps to the address that follows. If register
3 is <2 then it is not decremented and execution continues normally. |
| shift-K |
A0-AF
(-0 - -_) |
GSBI: Indirect subroutine call using the register number that follows.
If register number is 0-3 then the register is decremented after the call. |
|

|
| normal |
07 |
Number 7 |
| shift-F |
1C |
Sine of X |
| shift-K |
34 |
INT: Integer part of X |
|

|
| normal |
08 |
Number 8 |
| shift-F |
1D (1G) |
Cosine of X |
| shift-K |
35 |
FRAC: Fractional part of X |
|

|
| normal |
09 |
Number 9 |
| shift-F |
1E |
Tangent of X |
| shift-K |
36 |
Replaces X with the higher value of X and Y. Does not drop the stack.
Warning: If X or Y is 0 then the
result is always 0! Maybe a bug. |
|

|
| normal |
11 |
Substract Y-X |
| shift-F |
21 |
Square root of X |
| shift-K |
27 |
Undefined function. Causes ERROR |
|

|
| normal |
13 |
Divide Y/X. Note that when dividing by 0 the display will go blank for
about 5 (!) seconds before the error condition is displayed. |
| shift-F |
23 |
Reziprocal of X |
| shift-K |
29 |
Undefined function. Causes ERROR |
|

|
| normal |
04 |
Number 4 |
| shift-F |
19 |
Inverse sine of X |
| shift-K |
31 |
ABS: Absolute value of X |
|

|
| normal |
05 |
Number 5 |
| shift-F |
1A (1-) |
Inverse cosine of X |
| shift-K |
32 |
SIGN: Signum of X: -1 if X<0, 0 if X=0, 1 if X>0 |
|

|
| normal |
06 |
Number 6 |
| shift-F |
1E |
Inverse tangent of X |
| shift-K |
33 |
H-HM: Convert decimal hours to hours.minutes |
|

|
| normal |
10 |
Add Y+X |
| shift-F |
20 |
Number pi=3.1415... |
| shift-K |
26 |
HM-H: Convert hours.minutes to decimal hours
Example: 2.3030 -> 2.505 |
|

|
| normal |
12 |
Multiply Y*X |
| shift-F |
22 |
Sqare of X |
| shift-K |
28 |
Undefined function. Causes ERROR |
|

|
| normal |
01 |
Number 1 |
| shift-F |
16 |
Exponential of X |
| shift-K |
55 |
No function |
|

|
| normal |
02 |
Number 2 |
| shift-F |
17 |
Logarithm base 10 of X |
| shift-K |
56 |
No function |
|

|
| normal |
03 |
Number 3 |
| shift-F |
18 |
Natural logarithm of X |
| shift-K |
30 |
H-HMS: Convert decimal hours to hours.minutes/seconds |
|
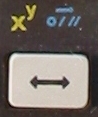
|
| normal |
14 |
Swap X and Y stack register |
| shift-F |
24 |
X to the power of Y. This is reversed comapred to the "normal" mode! |
| shift-K |
2A (2-) |
HMS-H: Convert hours.minutes/seconds to decimal hours
Example: 2.3030 -> 2.508333 |
|

|
| normal |
0E |
Push stack (ENTER) |
| shift-F |
0F (0_) |
Last-X register |
| shift-K |
3B (3L) |
RND: Create a random number 0<=X<1 |
|

|
| normal |
00 |
Number 0 |
| shift-F |
15 |
10 to the power of X |
| shift-K |
54 |
Programming instruction: NOP (no operation) |
|

|
| normal |
0A (0-) |
Decimal point. Note that a digit must be entered before the decimal
point! Also, the programming instruction "EXP ." seems to do surprising things. |
| shift-F |
25 |
Rotate stack down. |
| shift-K |
37 |
Perform binary operation Y AND X |
|

|
| normal |
0B (0L) |
Change sign of X |
| shift-F |
n/a |
Normal calculator mode (switches out of programming mode). |
| shift-K |
38 |
Perform binary operation Y OR X |
|

|
|

|
| normal |
0D (0G) |
Clear X-register |
| shift-F |
n/a |
Apparently clears the prefix key. Note that the prefix keys override
each other. So in order to clear the K prefix key press F and then CF. |
| shift-K |
3A (3-) |
Perform binary operation NOT X |
|